Tibial Interlocking Nail Benefits and Risks Explained?
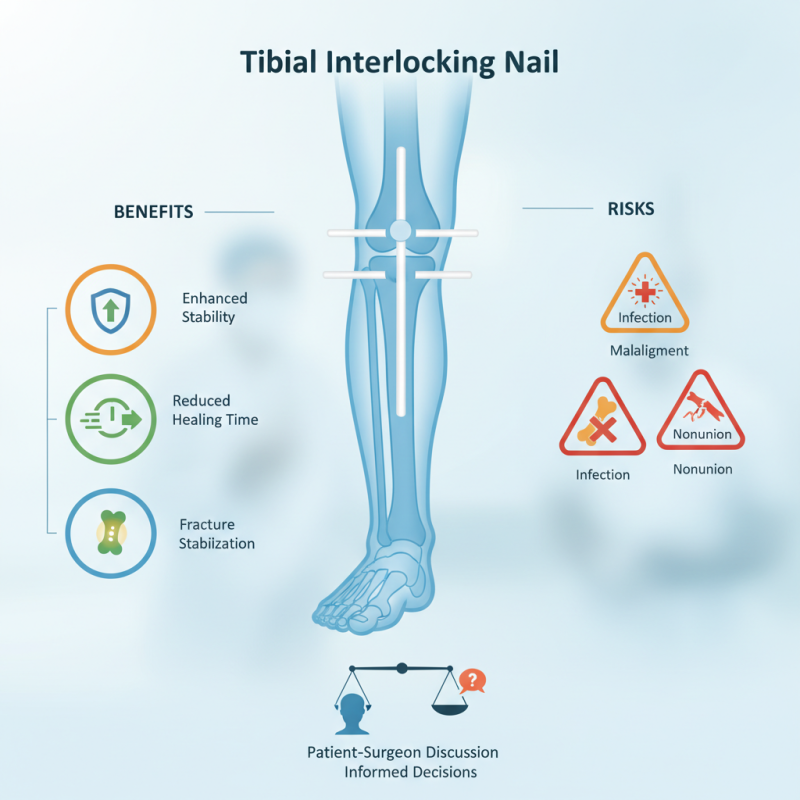
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is a commonly used device in orthopedic surgery. It is designed to stabilize fractures in the tibia, the larger bone in the lower leg. This nail is inserted into the medullary canal of the bone and secured with interlocking screws. This method offers advantages like enhanced stability and reduced healing time.
However, the use of the Tibial Interlocking Nail carries risks. Complications can include infection, malalignment, and nonunion of the bone. These factors can complicate recovery for some patients. It is essential to weigh the benefits against these risks. Patients and surgeons must consider individual circumstances carefully.
Understanding the Tibial Interlocking Nail involves acknowledging both its potential and its challenges. Each case is unique, and results may vary. Open discussions between patients and healthcare providers are vital. This approach can lead to better-informed decisions in managing tibial fractures.
Definition and Purpose of Tibial Interlocking Nail in Orthopedic Surgery
The tibial interlocking nail is a crucial tool in orthopedic surgery. It is designed to stabilize fractures of the tibia. This nail allows for early mobilization of the patient, reducing recovery time significantly. The interlocking feature helps to prevent rotation and provides axial stability. Data from the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma indicates that over 90% of patients achieve good to excellent results with this method.
However, there are risks involved. Complications can include infection, nonunion, and possible implant failure. Some patients report discomfort and limited range of motion after the procedure. It’s essential to weigh these risks against the benefits. Not every patient is a candidate for this approach. Careful assessment by an orthopedic surgeon is necessary.
**Tips:** Always discuss your concerns with your surgeon. Understanding potential complications can be empowering. Consider seeking a second opinion if you're unsure. If an interlocking nail is recommended, ask about recovery timelines and rehabilitation exercises. Engaging in this conversation can help you feel more in control.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Benefits and Risks Explained
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A tibial interlocking nail is an intramedullary device used to stabilize fractures in the tibia. |
| Purpose | To provide mechanical stability and promote healing of tibial fractures. |
| Benefits | Minimally invasive, reduces soft tissue damage, allows for early weight-bearing. |
| Risks | Risk of infection, non-union or malunion of the fracture, hardware failure. |
| Indications | Used in closed and open tibial fractures, especially in young and active patients. |
| Contraindications | Severe soft tissue injury, infection at the fracture site, or bone loss. |
| Recovery Time | Typically 3-6 months, depending on the fracture type and patient's health. |
| Post-Operative Care | Physical therapy, regular follow-ups, monitoring for complications. |
Advantages of Using Tibial Interlocking Nails for Fracture Management
Tibial interlocking nails are increasingly popular in fracture management. These devices provide stability to fractured tibias, allowing for better healing outcomes. They are particularly useful in complex fractures, where traditional treatments may fall short. Surgeons can align the bone fragments precisely with these nails. This often leads to fewer complications compared to plates or external fixators.
Using tibial interlocking nails also aids in early mobilization. Patients may begin rehabilitation sooner, which can accelerate recovery. The nail's design minimizes soft tissue damage, reducing infection risks. However, not every case is ideal for this method. Some patients might experience pain or discomfort post-surgery. Additionally, improper placement can lead to complications. Surgeons must weigh these factors carefully before proceeding. Each patient's situation is unique and requires thorough evaluation.
Potential Risks and Complications Associated with Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are becoming popular for treating complex tibial fractures. They provide stability, allowing for early mobilization. However, they also come with potential risks and complications that should not be overlooked. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, complications can occur in up to 15% of cases.
Infection is one of the most common risks associated with this procedure. Open fractures are particularly vulnerable. The rate of postoperative infection can reach 8%, significantly impacting recovery. Other complications include malunion or nonunion, which affect about 5% of patients. This often requires additional surgeries, causing physical and emotional strain.
Additionally, there's a risk of nerve or blood vessel damage during the insertion procedure. This can lead to long-term issues, like chronic pain or even disability. Many surgeons emphasize the importance of patient selection. Not all fractures are suitable for this method. A prudent approach can minimize risks and enhance outcomes.
Patient Selection Criteria for Tibial Interlocking Nail Procedures
When considering tibial interlocking nail procedures, patient selection is crucial. Ideal candidates often include those with stable, closed fractures. Data indicates that about 70% of these patients experience positive outcomes. However, not every case is suitable. Patients with open fractures or extensive soft tissue damage may face higher complications.
Certain criteria also dictate eligibility. Age plays a role, as younger individuals tend to heal faster. Studies show that patients under 50 years old yield better results, with roughly 80% achieving full recovery. Additionally, the presence of comorbidities, such as diabetes or osteoporosis, can complicate the healing process. About 60% of older adults may struggle with post-operative complications.
Despite these guidelines, perfection is not guaranteed. Some patients may experience prolonged pain or limited mobility post-surgery. Reports suggest that around 15% of individuals have ongoing discomfort even after optimal healing. These realities highlight the importance of thorough evaluations and realistic expectations before proceeding with the procedure.
Post-operative Care and Rehabilitation Following Tibial Interlocking Nail Surgery
Post-operative care after tibial interlocking nail surgery is crucial for optimal recovery. Patients typically need to follow strict guidelines. Engaging in early mobilization can enhance overall healing. According to the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery, early weight-bearing can improve outcomes in 70% of cases. Regular physical therapy sessions are essential. These sessions help restore function and strength to the leg.
Rehabilitation might take several months, depending on individual progress. During this period, complications can arise. Infection, for instance, occurs in about 5% of cases. Monitoring the surgical site daily is vital. Patients should keep an eye out for unusual swelling or discomfort. Additionally, adhering to prescribed medication is critical to manage pain effectively. It’s important to communicate with healthcare providers if symptoms worsen.
Diet also plays a role in healing. A balanced diet rich in protein can expedite recovery. Some studies suggest that Vitamin D is essential for bone regeneration. Still, many patients overlook dietary changes. They focus solely on physical activities. This can hinder overall recovery, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach in rehabilitation.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Surgery: Post-operative Pain Levels Over Time
This bar chart illustrates the average pain levels experienced by patients following tibial interlocking nail surgery over a month. Pain levels tend to decrease significantly within the first month, indicating effective post-operative recovery and pain management strategies.


